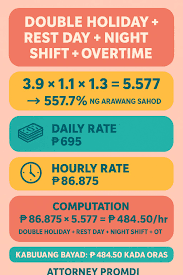
Proper computation of overtime, holiday, and night differential pay is essential for payroll compliance in the Philippines. Mistakes in these areas are among the most common reasons employers face DOLE inspections, employee complaints, and penalties.
This guide explains the rules for all types of overtime, holiday, and night shift pay in 2026, helping employers calculate payroll correctly and legally.
Why Accurate Pay Computation Matters
Payroll compliance protects your business and employees. Failure to correctly compute overtime, holiday, or night differential pay can result in:
- DOLE complaints or audits
- Labor disputes
- Employee dissatisfaction
- Financial penalties
For a complete payroll compliance overview, refer to our Payroll Compliance Guide for Employers in the Philippines 2026.
Overtime Pay Rules (2026)
Overtime is any work performed beyond the regular working hours (usually 8 hours/day).
Key rules:
- Overtime must be paid at 125% of the regular hourly rate for weekdays.
- Overtime on rest days or special holidays: 130–150% depending on the day type.
- Overtime on regular holidays: 200% of the regular rate.
Common mistakes:
- Paying regular rate instead of overtime rate
- Ignoring rest day or holiday premiums
Tip: Use our Salary Calculator Philippines to verify accurate overtime computations.
Rates may vary based on specific DOLE wage orders and applicable labor advisories. Employers should always verify current regulations.
Holiday Pay Rules
Employees are entitled to pay even if they do not work on certain holidays.
Types of holidays:
- Regular holidays – Fixed national holidays like New Year, Independence Day
- Special non-working holidays – Observances like Chinese New Year, Ninoy Aquino Day
Payment rules:
- Working on a regular holiday: 200% of the daily rate
- Working on a special holiday: 130% of the daily rate
- Not working: 100% of daily wage for regular holidays, no pay for special holidays unless company policy states otherwise
Night Differential Pay (2026)
Night differential applies for work between 10:00 PM and 6:00 AM.
Key rules:
- Night differential rate is 10% of the basic hourly rate
- Applies even if employee is working overtime or on holidays
Example:
If an employee works 2 hours of overtime at night on a weekday, both overtime premium and night differential must be applied.
Best Practices for Employers
To ensure compliance:
- Always follow updated DOLE and BIR rules
- Use reliable salary calculators for overtime, holiday, and night differential pay
- Document computations clearly in payroll records
- Train HR and payroll staff regularly
Employers should also ensure all earned overtime and holiday pay are included when processing employee separation. Refer to our Final Pay Computation Guide for Employers (2026).
Check our guides for reference:
Common Payroll Mistakes to Avoid
- Paying regular rate instead of overtime/holiday rates
- Ignoring night differential pay
- Failing to properly document calculations
- Applying outdated contribution tables or rules
Final Thoughts
Correctly computing overtime, holiday, and night differential pay is not optional. Accurate payroll ensures employee satisfaction, avoids DOLE complaints, and strengthens trust in your business.
Stay compliant in 2026 by following this guide and using the recommended payroll tools.